At first glance, all disc brake pads are very similar – they have the same basic shape and more or less claim to do the same job. However, their simple appearance hides the complex manufacturing process that’s needed to develop a high-quality brake pad.
A key component of the brake pads is the make-up of the brake compound, this is the friction material that plays the all-important role of meeting and coupling with the disc rotors to slow the vehicle down once the brakes are applied
The ingredients used to develop these friction compounds varies depending on the manufacturer, but general ingredients include a mixture of fibres, functional fillers, friction modifiers, lubricants, and resin binders. Differences in the source materials will result in the pads having different performance characteristics.
How much noise pads generate, the level of dust they release, their durability and their stopping performance, are all greatly influenced by the compound they use and ingredients, and of course this makes some brake pads more suitable for certain applications and driving conditions than others.
In the case of Bendix pads, the braking compounds can be categorised into three main groups, Ceramic / Non-Asbestos Organics (NAO), Low Metallic (Low Met) and Semi Metallic (Semi-Met). Here’s an overview of each.
Ceramic/Non-Asbestos Organics (NAO)
Bendix Ceramic pads, use a combination of organic materials such as synthetic glass fibres, aramid fibres, and natural fibres as the main reinforcing ingredients and include several organic modifiers as well as metals such as copper, but no steel, this combination being applied to further finetune the formulation depending on the make and model of the vehicle.
Bendix offers a wide selection of Ceramic / NAO-based pads, including the General CT range.
The manufacturing process used for these pads consists of computer controlled presses that heat and compress the material mix cyclically to form the pad. The processing method employed by Bendix dramatically increases the durability of the pads while also delivering low levels of dust, noise and rotor wear, while still providing a consistent pedal feel for the driver. Ceramic materials are the core of the Bendix range which are available within the Bendix General CT, EV-Hybrid, Euro+, Ultimate+ and Ultimate 4WD products.
Low-Metallic (Low-Met)
Low-Met brake pads contain some ceramic materials but are designed for performance and high-speed driving styles, so contain high levels of mineral abrasives to provide additional stopping power for optimal performance.

Low-Met pads such as the Bendix Street, Road and Track range feature high levels of mineral abrasives for additional stopping performance.
More spirited driving and more aggressive or regular braking leads to increased temperatures which can cause brake fade, and for these driving scenarios, the low-met compounds are used in the Bendix Street Road & Track range for performance stopping.
Semi-Metallic (Semi-Met)
Semi Metallic brake pads contain high amounts of steel and iron that along with specific binding materials, provide consistency of stopping power in high temperature conditions.
Vehicles that normally operate with heavier loads (elevated pad temperatures) over longer periods including utilities, vans and trucks, need pads that perform consistently when hot while also being longer lasting.
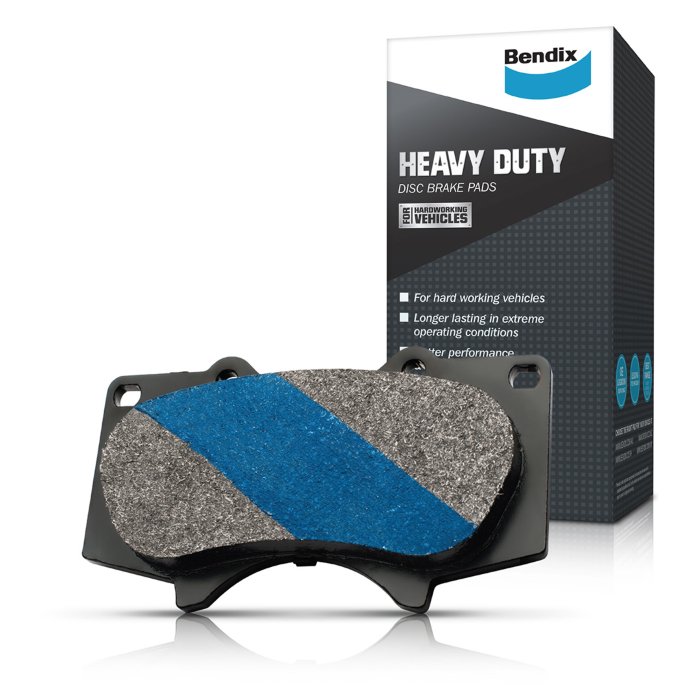

For long hour use under heavy loads, conditions normally experienced by commercial vehicles, the Bendix Heavy Duty semi-met pads use more steel and iron to deliver high temperature performance and longevity.
For these applications, brake pads from the Bendix Heavy Duty range are well suited – they feature a specifically designed semi metallic compound. This combination of materials in conjunction with proprietary processing, results in a high integrity of the brake pad at temperature without lowering rotor life.
For further information:
For more information free call the Bendix Brake Advice Centre on 1800 819 666 or +61 3 5327 0211 from overseas (8am-5pm Monday to Friday EST), e-mail us at: [email protected] or visit our website www.bendix.com.au
This article is brought to you by BENDIX