
Grease is formed by emulsifying liquid lubricant in a thickening agent like soap. The liquid lubricant in the grease generally is mineral oil or synthetic oil.
The key difference between oil and grease is the addition of thickening agent, typically a soap in grease. Generally, in room temperature and pressure, oil is in liquid form while grease would be in solid or semi-solid form.
Grease exhibits shear-thinning or pseudo-plastic fluid characteristic, which means that the viscosity of the fluid is reduced under shear. Once adequate force applied to shear the grease is achieved, the viscosity drops and approaches that of the base lubricant use in the formation of the grease.
Soap is the most common thickener or emulsifying agent for grease. The choice of the soap plays important roles in the performance of the grease like the operating temperature, water resistance, and chemical stability. Similarly, like liquid lubricants, grease is added with specific additives to improve the performance
Like liquid lubricants, greases also are available in various grades and forms. In grease, the most important criterion for selection is the NLGI grade. NLGI grade is the measure of the consistency or relative hardness of a grease used for lubrication, as specified by the standard classification of lubricating grease established by the National Lubricating Grease Institute (NLGI). The below table shows the NLGI number and compares each grade with everyday products of similar consistency.
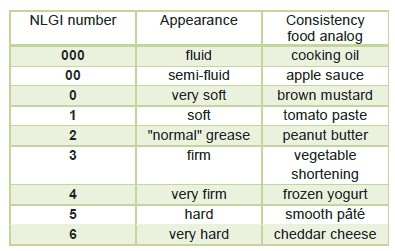
The most common grease grade in automotive and industrial application is NLGI 2. This is followed by NLGI 1 and NLGI 3 grade grease. Other NLGI grades grease are usually required in other special application.
After selecting the right NLGI grade, the next evaluation is viscosity of the base oil in the grease. The base oil viscosity is measured in centistokes (cSt) at 40°C. Following rule of thumb, the higher the bearing/ component speed, the lower the base oil viscosity required. Thicker base oils are used in slower moving, heavily loaded applications.
Greases are usually formulated using mineral grade base oil. For grease formulated with synthetic base oil, it would enable the grease to reach higher or lower operating temperatures as well as wider operating temperature range compared to mineral base grease. In addition, synthetic base oil grease is used in application where extended relubrication intervals are required.
To improve performance, greases are improved by using additives. Example of additives are oxidation and rust inhibitors, extreme pressure additives, antiwear and friction-reducing additives.
The most widely used soap are lithium and calcium. Grease with lithium is preferred in general application as it has high dropping point and stable when carrying high load. Calcium grease is preferred for marine application due to its excellent water resistivity.
Castrol’s specially formulated range of high-performance greases provide outstanding protection in all operating conditions and applications. We have developed some of the most advanced and high performing greases in the world, including for the International Space Station and the Mars curiosity rover. Technical team at Castrol have the experience and knowledge to help you make the most optimum choice on grease selection.

This article is brought to you by Castrol